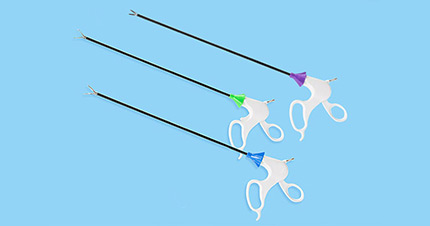
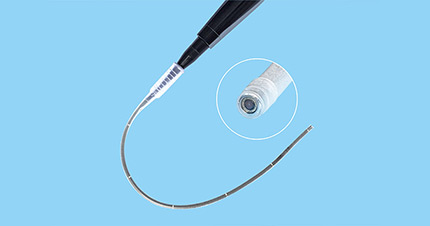
Taking you understand surgical trocars
 Feb 06, 2023|
Feb 06, 2023| View:921
View:921The coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is affecting the entire global marketplace. In addition to the cost of human lives, the impact of virus transmission on the global economy is just beginning to be recognized and is having a profound impact on the world's technology supply chain, and a profound impact on the world's technology supply chain. One of the most profound impacts has been on the medical industry. The surgical trocar is a medical device in the medical technology industry that provides access to the abdominal cavity during laparoscopic procedures, of which disposable surgical trocars and reusable surgical trocars are the more common types.
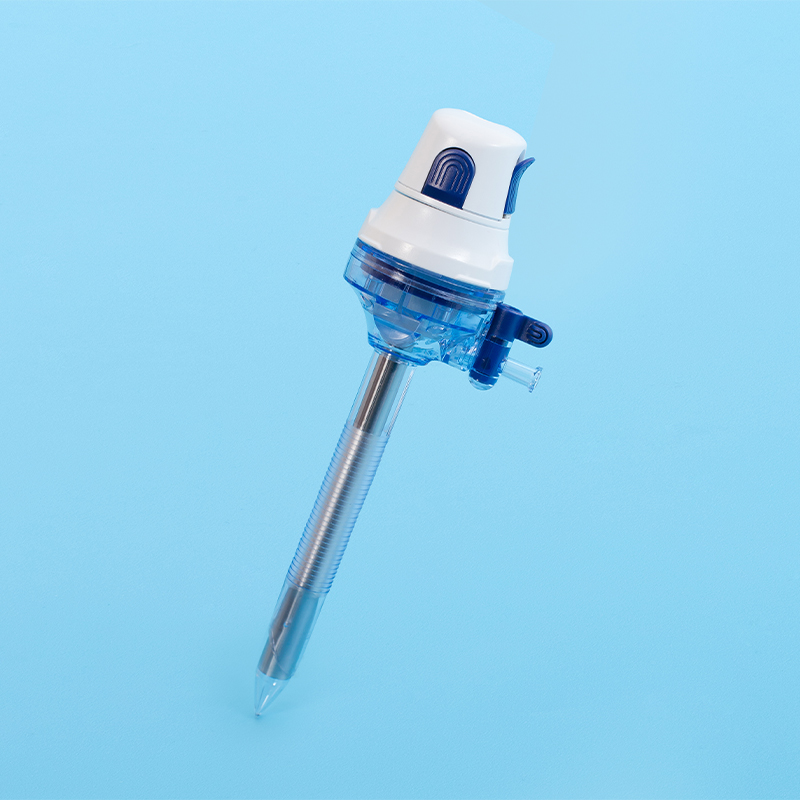

1. General composition.
Disposable surgical trocars and reusable surgical trocars share the following configurations.
(1) Sleeve.
This is the operating tubing sleeve, with outer and inner diameters varying by material thickness and tubing size varying by manufacturer. For 5 mm surgical trocars, the inside diameter ranges from 4.5 to 5.5 mm. It is important to know the inside diameter size because if the tube diameter is too large and the instrument used does not have a valve, gas leakage may occur; if the tube diameter is just the same as the needle holder, the tip and holder cannot pass through the tube at the same time; 5 mm holders require a tube inside diameter of 5.5 mm to allow the tip and holder to pass together; the outside diameter is also limited. The outer diameter is also limited because it is related to the size of the cut; the ideal sleeve must be thin-walled to allow the inner and outer diameters to be similar.
(2) Tip.
The surgical trocar tip helps pass through the abdominal wall into the peritoneal cavity and is available in the following types of tips: conical, blunt, pyramidal, etc. The sharp tip cuts through the abdominal wall, and the blunt tip pulls away from the tissue to gain access to the peritoneal cavity; these tips are usually related to the surgeon's training.
(3) Sealing system.
The gas pressure that builds up the pneumoperitoneum is greater than the surrounding atmospheric pressure, and to avoid gas leakage from the open position, surgical trocars are built with a valve that allows insertion of the instrument without leakage; different valve systems are available, such as ruffled valves, piston (flapper) valves, duckbill valves, and magnetic ball valves.
(4) Inflation port.
Many surgical trocars are equipped with an opening for inflation into the body cavity of the surgical site; some surgical trocars do not have such an opening, especially those <= 5 mm in diameter.
2. Reusable surgical trocars.
At the beginning of imaging laparoscopy (1987-1990), most surgical trocars used reusable cannulae, which consisted of several detachable parts, some with an inflatable sheath used in conjunction with electrocautery; these surgical trocars had the advantage of reducing the cost of the procedure, but cleaning and sterilization required laborious disassembly and reassembly and inevitably could lead to mechanical damage; the high cost of cleaning and sterilization, as well as the reduction of the cost of these surgical trocars, were not sufficient. The high cost of cleaning and sterilization and the reduced dependability of these surgical cannulas have led many surgeons to switch to disposable instruments.
3. Disposable surgical trocars.
Disposable surgical trocars are more costly when performing multiple laparoscopic procedures, but they offer many benefits over reusable instruments.
(1) Human resources are saved, and there is no need for maintenance.
(2) Available in various forms with diameters ranging from 2 mm to over 30 mm to accommodate cricoid staples for performing anastomoses.
(3) Sealed retentive flaps fit 2 to 12 mm instruments without the need for adjustment or the addition of an adapter.
(4) Most disposable cannulas with cutting tips have a safety system that covers the tip or blade as it enters the abdominal cavity, thus minimizing organ damage.
(5) Some trocar sleeves are transparent, allowing visualization of structures around the trocar (e.g., the abdominal wall), which helps to correct the position of the trocar tip in the abdominal cavity and also increases the field of view to identify other structures or instruments that may not be visible.
4. Fixation system for surgical trocars.
(1) Principles.
Ideally, surgical trocars must be stabilized in the peritoneal cavity to reduce the risk of slipping into the peritoneal cavity. Some manufacturers have developed surgical trocars with a patterned appearance to help anchor them in the peritoneal cavity. Others have a variety of systems that can anchor the trocar to the abdominal wall. This is particularly useful when openly establishing a pneumoperitoneum, as this is needed for situations where the entry position is large and less fixable.
(2) Internal balloon and external pressure.
This trocar system creates a pneumoperitoneal seal after the trocar insertion via the open approach. The tip of the surgical trocar is built with an inflatable balloon that is inflated after the trocar is introduced into the abdominal cavity and then pulled back against the abdominal wall to compress the opening and lock the trocar with a foam ring to achieve external pressure.
(3) Spiral wire.
Many systems use a spiral wire to minimize or eliminate the chance of the trocar slipping out of the perforated position. The groove of the spiral wire must match the diameter of the incision to allow the top of the wire to bite into the tissue and avoid trocar slippage. There are two systems as follows.
(a) The surgical trocar sleeve itself is wired.
b) The coil is fixed to a smooth trocar sleeve. The advantage of this system is that it allows simple adjustment of the surgical trocar position.
(4) Money bag suture fixation.
If the trocar accidentally leaks out of the abdomen, a money-bag suture is used around the insertion site. It can also be secured to the protruding part of the trocar (e.g., the piston) to avoid slippage.
The above is the knowledge about surgical trocars. If you need more detailed information, welcome to contact us!



 molly@surgitoolssh.com
molly@surgitoolssh.com